The Bureau of Ocean Energy Management's (BOEM) Environmental Studies Program (ESP) has been supporting research through the National Oceanographic Partnership Program (NOPP) since 1999, with nearly 40 partnership opportunities that leveraged nearly $40 million dollars in funding. Through NOPP, the ESP has partnered with the National Science Foundation (NSF), Office of Naval Research (ONR), Department of Energy (DOE), US Geological Survey (USGS), and several program offices at the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA).
NOPP is a highly successful, collaborative program that facilitates partnerships between federal agencies, academia, industry, and tribal communities to advance ocean science research and education. Through this collaboration, federal agencies with overlapping mission priorities can better leverage their limited resources to accomplish objectives that would otherwise be too large for any single agency to achieve acting on its own.
Research includes marine mammal behavior and acoustics; exploration and research of deepwater habitats (including coral, sponge, and chemosynthetic communities); wave, current, and wind modeling for renewable energy; archaeological and biological analysis of shipwrecks in the Gulf of Mexico from World War II, and ecosystem research in the Arctic.
Excellence in Partnering Awards
Excellence in Partnering Awards are presented annually to research teams that best exemplify the NOPP partnership objectives: the project’s commitment to partnering, the success of the partnership effort, and the impact of the partnership on knowledge and stewardship of our ocean. Following are the NOPP awards that have included BOEM participation and support.
2019 Marine Arctic Ecosystem Study (MARES)
Marine Arctic Ecosystem Study (MARES)
Lead Principal Investigator (PIs): Dr. Francis Wiese (Stantec).
The study involved federal, academic, private, tribal, and state government sectors in the US and Canada with the goal of enhancing our understanding of the structure and functioning of the Arctic marine ecosystem in the eastern Beaufort Sea. MARES, which started in 2014, stems from increased attention to climate change, energy development, and sustainability in the Arctic region.
|
(MARES photo) |
|
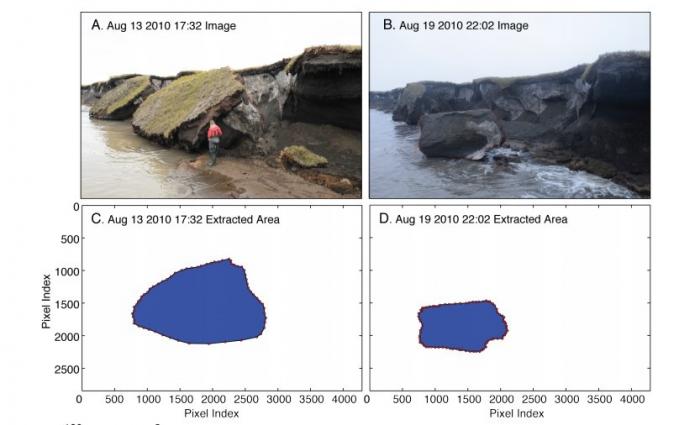
2017 Gulf of Mexico SCHEMA Study
Gulf of Mexico SCHEMA Study
Lead PIs:
Leila J. Hamdan (University of Southern Mississippi); Melanie Damour (Bureau of Ocean Energy Management)
Co-PIs:
Robert Church (Oceaneering, Inc.);
Lisa A. Fitzgerald (Naval Research Laboratory); Christopher Horrell (Bureau of Safety and Environmental Enforcement);
Sheli Smith (The PAST Foundation);
Daniel Warren, (P&C Scientific, LLC)
In this study, the Gulf of Mexico Shipwreck Corrosion, Hydrocarbon Exposure, Microbiology, and Archaeology Project (GOM-SCHEMA), a multi-disciplinary team of 33 scientists and university students examined the effects of Deepwater Horizon spill-related oil and dispersant exposure on deepwater shipwrecks and their microbial communities.
The scientists represented the fields of marine archaeology, microbial ecology, molecular biology, geochemistry, geology, and corrosion studies.
|
|
|
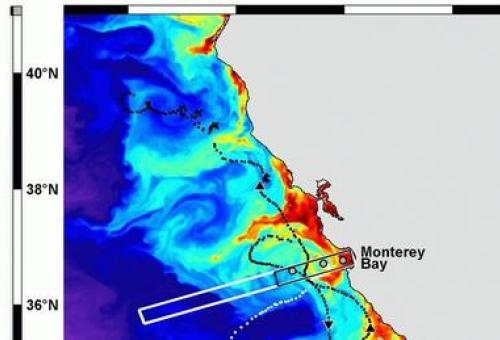
2016 Marine Sanctuaries Observation Network (MBON)
Marine Sanctuaries Observation Network (MBON)
Lead PIs:
Frank Muller-Karger (University of South Florida);
Dr. Bob Miller (University of California, Santa Barbara);
Dr. Katrin Iken (University of Alaska, Fairbanks)
Co-PIs:
Francisco Chavez (Monterey Bay Aquarium Research Institute);
Scott Doney and Maria Kavanaugh (Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution);
Enrique Montes (University of South Florida);
Steve Gittings (NOAA Office of National Marine Sanctuaries)
The “National Marine Sanctuaries and Sentinel Sites for a Demonstration Marine Biodiversity Network” (MBON) project sought to systematically observe spatial and temporal changes in the biological diversity at the ecosystem scale in two marine conservation areas—the Florida Keys and the Monterey Bay (California) National Marine Sanctuaries. The study also was designed to evaluate various observational methods used to monitor changes in marine biodiversity in these areas.
The primary methods evaluated were e-DNA and a suite of remote sensing technologies. Novel eDNA techniques and ongoing observations evaluated habitat diversity and the diversity of lower to higher trophic levels, defined the variables responsible for significant change in biodiversity indices, and helped identify invasive species. Multidisciplinary remote sensing was used to extend the spatial footprint of the data collected in situ (at specific locations). These observations will help construct conceptual and forecast models of the relationships between human activity, natural environmental variability including climate change, and ecosystem structure at multiple trophic levels. This effort was structured to address the Convention on Biological Diversity and to assess ecosystem health, advance protection of marine resources, and promote conservation.
|
|
|
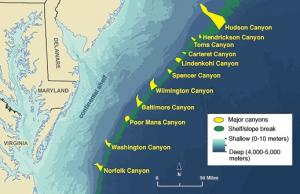
2015 Atlantic Canyons: Pathways to the Abyss
Atlantic Canyons: Pathways to the Abyss
Lead PIs:
Steve W. Ross (University of North Carolina Wilmington);
Sandra Brooke (Florida State University);
Stephen Viada (Continental Shelf Ocean Sciences Inc.)
The 2015 Excellence in Partnering Award recognized the project team for the Atlantic Canyons: Pathways to the Abyss study.
The project brought together 17 organizations to investigate the Norfolk and Baltimore Canyons from 2011 to 2013. Researchers found unexpected, extensive deep-water coral ecosystems, a vast methane seep ecosystem, and large swaths of chemosynthetic mussel communities.
The researchers identified over 125 species of fish, documented historically important shipwrecks off Virginia’s coast, and deployed innovative sensing technologies to monitor oceanographic characteristics. In addition to the data and reports, project deliverables included a video and other educational and communication materials documenting the research and discoveries. BOEM, NOAA and USGS funded the research.
|
|
|