Distribution:
From the east coast of North America
through the eastern Gulf of America
Ecosystem:
Mostly salt water, but spawns in freshwaters
Feeding Habits:
Benthic feeder
Taxonomy:
Family Acipenseridae
Class Actinopterygii
Credit:
Ryan Hagerty/USFWS
Overview and Physical Characteristics
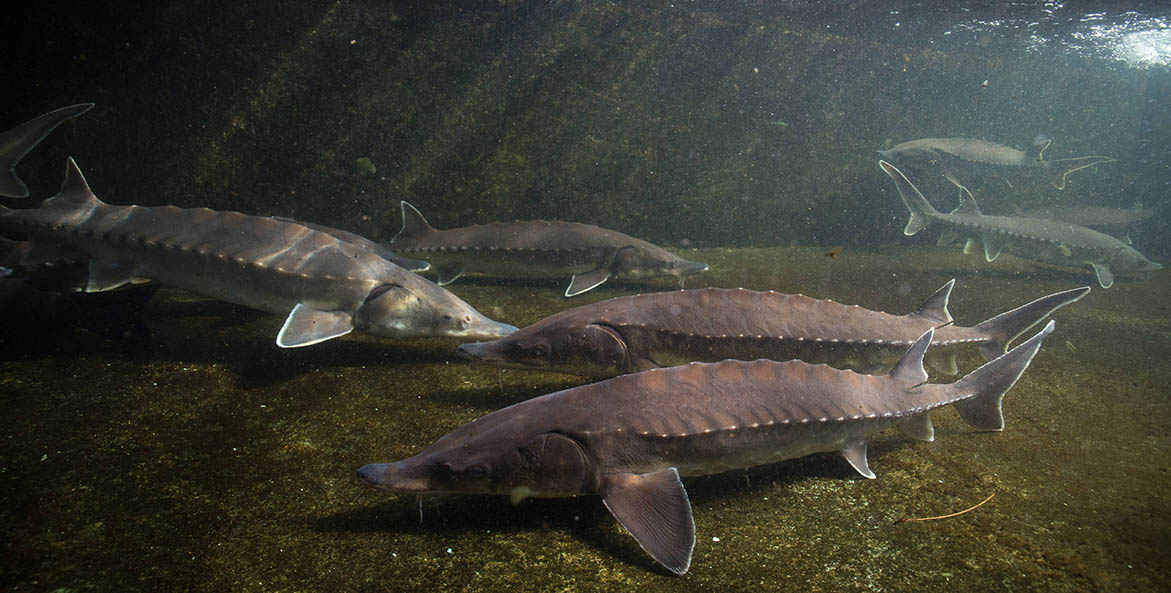
Fossil records from over a 120 million years ago have preserved the elongated, torpedo-shaped body of a sturgeon from a time when the Earth consisted of only two supercontinents instead of the familiar seven continents we know today. Epochs-old sturgeon fossils are remarkably the same as today’s Atlantic sturgeon—a living relic from prehistoric times.
The Atlantic sturgeon’s (Acipenser oxyrinchus oxyrinchus) body is covered with five rows of bony plates called scutes, which look like the armor found on certain dinosaur fossils. Atlantic sturgeon have long, whisker-like feelers along their mouths and pointed snouts called barbels, which they drag along the bottom to detect potential prey. These ancient fish can live up to 70 years, growing to 16 feet long and weighing 800 pounds.
Habitat and Distribution
Atlantic Sturgeon can be found from the mouth of the St. Lawrence River in Canada to the coasts of southeastern Florida, with a subspecies living in the eastern waters of the Gulf. They live in a variety of climates, reflecting the Atlantic sturgeons’ innate versatility in adapting to the various conditions of different ecosystems. They are anadromous, which means that Atlantic sturgeon spend most of their lives in salt water, although they venture into freshwater rivers and streams to spawn.
Ecosystem
The Atlantic sturgeon is a benthic feeder, meaning that they find their food on the bottom of bays and rivers where they reside. Their diet consists primarily of worms, crustaceans, and small fish, which they suck up with their vacuum-like snouts. As bottom feeders the Atlantic sturgeon are essential to ecosystem health, helping aerate the bottom silt and cycle nutrients through the ecosystem.
Behavior and Reproduction
Atlantic sturgeon are notable for their delayed maturity—males reach breeding age between 8-12 years while female achieve their breeding potential between 10-20 years. While spawning, a female sturgeon will lay hundreds of thousands of eggs in the gravelly or sandy bottoms of freshwater rivers. A male sturgeon will simultaneously release milt to fertilize the eggs.
Not all Atlantic sturgeons spawn annually, with some only breeding every two to six years. Atlantic sturgeon only spawn in oxygen-rich waters, which are crucial for the survival of their young. Juvenile sturgeon remain in their freshwater environment for 1-6 years before migrating to the ocean.
Fun Fact
Although it’s uncommon behavior for large bottom-feeding fish, Atlantic sturgeon have been known to leap out of the water. The reasons for this behavior are not fully known.
Some theories posit that they leave to water to loosen parasites on their skin; others suggest they are pursuing airborne prey; and some speculate that Atlantic sturgeon propel themselves out of the water just because it feels good. The most recent theory, offered by a group of researchers in Florida, is that a sturgeon’s leap and subsequent splash is a type of group communication, for a species that exist primarily in a dark and murky bottom environment, letting other sturgeon know just where the rest of the group is hanging out.
For More Information
Learn About Recent BOEM Studies
More Information
This story is part of the “Unleashing the Science” series, showcasing how bureaus within the Department of the Interior produce and apply science to ensure responsible management decisions for our planet now and for the future.
--BOEM--
The Department of the Interior’s Bureau of Ocean Energy Management (BOEM) manages development of U.S. Outer Continental Shelf (OCS) energy, mineral, and geological resources in an environmentally and economically responsible way.